

| Home | ||||
Vaccine Testing
|
||||
| Research Materials |
||||
| Links | ||||
| Contacts | ||||
| Frequently Asked Questions | ||||
| Publications |
Pre-Clinical Animal Models for Testing Novel Experimental Vaccines Against Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Two animal model systems are used to test experimental vaccines submitted to the contract. These include the mouse and guinea pig models.
Short-term mouse model
C57BL/6 mice are vaccinated with the experimental vaccine according to the appropriate protocol and then rested for 4 to 6 weeks. 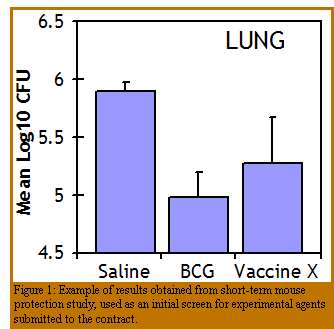 Immunized mice are infected with a low dose aerosol (50-100 CFU) of virulent M. tuberculosis and protection is evaluated by assessing the number of viable bacilli 30 days post challenge.
Immunized mice are infected with a low dose aerosol (50-100 CFU) of virulent M. tuberculosis and protection is evaluated by assessing the number of viable bacilli 30 days post challenge.
Viable counts are performed on the lung and spleen of mice by homogenizing the organs and plating serial 10-fold dilutions on 7H11 agar plates. Plates are incubated for up to 21 days and the number of colony forming units per organ determined.
BCG vaccinated mice have approximately 1Log10 protection in their lung and spleen when compared to PBS-treated mice.
Short-term guinea pig model
Out-bred Hartley guinea pigs are vaccinated with the experimental vaccine according to the appropriate protocol and then rested for 8 to 10 weeks. Immunized guinea pigs are infected with 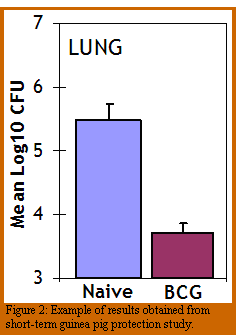 a low dose aerosol (10-30 CFU) of virulent M. tuberculosis and protection is evaluated by assessing the number of viable bacilli 30 days post challenge.
a low dose aerosol (10-30 CFU) of virulent M. tuberculosis and protection is evaluated by assessing the number of viable bacilli 30 days post challenge.
Viable counts are performed on the lung and spleen of guinea pigs by homogenizing the organs and plating serial 10-fold dilutions on 7H11 agar plates. Plates are incubated for up to 21 days and the number of colony forming units per organ determined. Lung and spleen segments are also taken for histological analysis.
BCG vaccinated guinea pigs have approximately 2-3Log10 protection in their lung and spleen when compared to PBS-treated guinea pigs. In addition, BCG vaccinated guinea pigs have well defined granulomas when compared to unvaccinated animals (Figure 2).
Long-term guinea pig model
Out-bred Hartley guinea pigs are vaccinated with the experimental vaccine according to the appropriate protocol and then rested for 8 to 10 weeks. Immunized guinea pigs are then infected with a low dose aerosol (10-30 CFU) of virulent M. tuberculosis. Guinea pigs are weighed 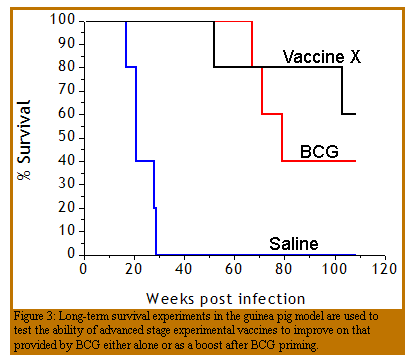 weekly and monitored daily for signs of disease (such as increased respiration and failure to thrive). Unvaccinated guinea pigs succumb to infection from 20 to 25 weeks post challenge, while BCG vaccinated guinea pigs survive for 50 to 55 weeks post challenge.
weekly and monitored daily for signs of disease (such as increased respiration and failure to thrive). Unvaccinated guinea pigs succumb to infection from 20 to 25 weeks post challenge, while BCG vaccinated guinea pigs survive for 50 to 55 weeks post challenge.
At necropsy, the lung and spleen are assessed for the number of CFU and the extent of pathology.
The relative protection of experimental vaccines is compared to BCG vaccinated animals.
Immunology of vaccination
Assessment of the immune response after vaccination can be performed and is dependent on the specific needs of the applicant.
Mouse experiments can be performed to investigate vaccine-induced immune responses.
Due to the low number of reagents currently available immunology studies in the guinea pig are currently limited.
Other animal models
The NIH contract is continually developing novel animal models to test vaccine candidates.